This website is intended for use by US healthcare professionals only.
Resources
Support materials for Tralement (trace elements injection 4*, USP) and Multrys (trace elements injection 4*, USP)

Be in your element with the materials you need to help provide more complete parenteral nutrition (PN).

Click here to explore the American Regent Trace Elements Reference Guide
Helpful Links
Our Commitment
With more than 50 years of specialty hospital injectable experience, American Regent has been committed to supporting the clinical community with responsive, reliable service.
ASPEN
View resources from the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN). ASPEN is dedicated to the science and practice of clinical nutrition.
INDICATIONS AND IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
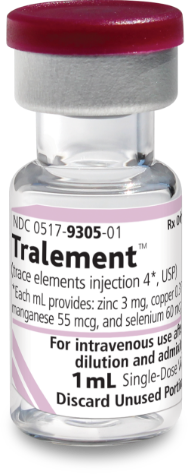
Tralement (trace elements injection 4*, USP)
*Each mL of Tralement contains zinc 3 mg, copper 0.3 mg, manganese 55 mcg, and selenium 60 mcg.
For intravenous use
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Tralement is indicated for adult and pediatric patients weighing at least 10 kg as a source of zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Tralement is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to zinc or copper.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates: Pulmonary vascular precipitates causing pulmonary vascular emboli and pulmonary distress have been reported in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the infusion and initiate a medical evaluation.
- Vein Damage and Thrombosis: Tralement must be prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solution. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. In addition, consider the osmolarity of the final parenteral nutrition solution in determining peripheral versus central administration. Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or more must be infused through a central catheter. The primary complication of peripheral access is venous thrombophlebitis.
- Neurologic Toxicity with Manganese: Monitor patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition solutions containing Tralement for neurologic signs and symptoms, and routinely monitor whole blood manganese concentrations and liver function tests. Discontinue Tralement and consider brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) if toxicity suspected.
- Hepatic Accumulation of Copper and Manganese: If a patient develops signs or symptoms of hepatic or biliary dysfunction during the use of Tralement, obtain serum concentrations of copper and ceruloplasmin as well as manganese whole blood concentrations. Consider using individual trace element products in patients with hepatic and/or biliary dysfunction.
- Aluminum Toxicity: Tralement contains aluminum that may be toxic. Increased risk in patients with renal impairment. Preterm infants, including preterm neonates, are particularly at risk.
- Monitoring and Laboratory Tests: Monitor blood zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium concentrations, fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count, and coagulation parameters.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions with Zinc and Copper: If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Tralement and initiate appropriate medical treatment.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions were identified in clinical studies or post-marketing reports. Given that some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions with other components of parenteral nutrition solutions:
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates
- Vein damage and thrombosis
- Aluminum toxicity
Adverse reactions with the use of trace elements administered parenterally or by other routes of administration:
- Neurologic toxicity with manganese
- Hepatic accumulation of copper and manganese
- Hypersensitivity reactions with zinc and copper
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy - Risk Summary - Deficiency of trace elements may result in adverse pregnancy and fetal outcomes.
Lactation - Risk Summary - Zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium are present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered, along with the mother’s clinical need for Tralement and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Tralement or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use - Refer to Full Prescribing Information for dosing. Do not supplement Tralement with additional manganese. Tralement is not approved for use in pediatric patients weighing less than 10 kg because the product does not provide an adequate dosage of zinc, copper, or selenium to meet the needs of this subpopulation and exceeds the recommended dosage of manganese.
Hepatic Impairment - Hepatic accumulation of copper and manganese have been reported with long-term administration in parenteral nutrition. For patients with cholestasis, biliary dysfunction, or cirrhosis, monitor hepatic and biliary function during long-term administration of Tralement.
OVERDOSAGE - There are reports on overdosage in the literature for the individual trace elements. Management of overdosage is supportive care based on presenting signs and symptoms.
Important Administration Information
Tralement is supplied as a single-dose vial for admixture use only. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, Tralement must be transferred to a separate parenteral nutrition container, diluted, and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solution.
Overview of Dosing
- Prior to administration of parenteral nutrition solution containing Tralement, correct severe fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disorders.
- The dosage of the final parenteral nutrition solution containing Tralement must be based on the concentrations of all components in the solution, the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and the contribution of oral or enteral intake.
Tralement is recommended only for patients who require supplementation with all four of the individual trace elements (ie, zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium).
For additional safety information, please see Full Prescribing Information.
You are encouraged to report Adverse Drug Events (ADEs) to American Regent, Inc. at 1-800-734-9236, or to the FDA by visiting fda.gov/safety/medwatch or calling 1-800-FDA-1088.
REF-1535 (v7.0) 2/2023
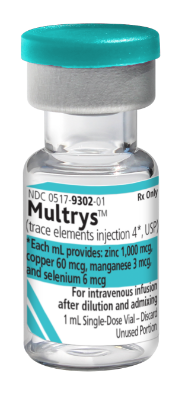
Multrys (trace elements injection 4*, USP)
*Each mL of Multrys provides zinc 1,000 mcg, copper 60 mcg, manganese 3 mcg, and selenium 6 mcg.
For intravenous use
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Multrys is a combination of trace elements (zinc sulfate, cupric sulfate, manganese sulfate, and selenious acid) indicated in neonatal and pediatric patients weighing less than 10 kg as a source of zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to zinc or copper.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates: Pulmonary vascular precipitates causing pulmonary vascular emboli and pulmonary distress have been reported in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the parenteral nutrition infusion and initiate a medical evaluation.
Vein Damage and Thrombosis: Multrys must be prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solution. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. In addition, consider the osmolarity of the final parenteral nutrition solution in determining peripheral versus central administration. Solution with an osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter. The infusion of hypertonic nutrient solution into a peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage, and/or thrombosis.
Neurologic Toxicity with Manganese: Monitor for clinical signs and symptoms of neurotoxicity, whole blood manganese concentrations, and liver function tests. Discontinue Multrys and consider brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) if toxicity is suspected. Monitor patients for cholestasis or other biliary liver disease.
Hepatic Accumulation of Copper and Manganese: If a patient develops signs or symptoms of hepatobiliary disease during the use of Multrys, obtain serum concentrations of copper and ceruloplasmin as well as manganese whole blood concentrations; consider using individual trace element products in these patients.
Aluminum Toxicity: Multrys contains aluminum that may be toxic. Patients with renal impairment and preterm infants, including preterm neonates, are particularly at risk.
Monitoring and Laboratory Tests: Monitor blood zinc, copper, and selenium serum concentrations, whole blood manganese concentration, fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count, and coagulation parameters.
Hypersensitivity Reactions with Zinc and Copper: If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue and initiate appropriate medical treatment.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions were identified in clinical studies or post-marketing reports. Given that some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions with other components of parenteral nutrition solutions:
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates
- Vein damage and thrombosis
- Aluminum toxicity
Adverse reactions with the use of trace elements administered parenterally or by other routes of administration:
- Neurologic toxicity with manganese
- Hepatic accumulation of copper and manganese
- Hypersensitivity reactions with zinc and copper
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Hepatic Impairment - Hepatic accumulation of copper and manganese have been reported with long-term administration in parenteral nutrition. For patients with cholestasis, biliary dysfunction, or cirrhosis, monitor hepatic and biliary function during long-term administration of Multrys.
OVERDOSAGE
There are reports on overdosage in the literature for the individual trace elements. Management of overdosage is supportive care based on presenting signs and symptoms.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Important Administration Information
Multrys is supplied as a single-dose vial. Prior to administration, Multrys must be transferred to a separate parenteral nutrition container, diluted, and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solution.
Overview of Dosing
Prior to administration of parenteral nutrition solution containing Multrys, correct severe fluid, electrolyte and acid-base disorders. It is recommended only for patients who require supplementation with all four of the individual trace elements (zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium). Multrys is not recommended for patients who may require a lower dosage of one or more of the individual trace elements. Avoid additional manganese supplementation with Multrys use.
For additional safety information, please see Full Prescribing Information.
You are encouraged to report Adverse Drug Events to American Regent, Inc. at 1-800-734-9236, or to the FDA by visiting fda.gov/safety/medwatch or by calling 1-800-FDA-1088.
REF-1826 (v5.0) 6/2021